Do not Fear With Ovarian Cysts
 Each
woman would be afraid if you hear disease called ovarian cysts. The disease is
becoming a scary thing because of its presence in the body can develop into
cancer and lethal.
Each
woman would be afraid if you hear disease called ovarian cysts. The disease is
becoming a scary thing because of its presence in the body can develop into
cancer and lethal.
Basically,
ovarian cysts are not dangerous. That made it evolve into malignant when its
presence is not handled properly.
Detection of Early as
Possible
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled bumps that develop on the ovaries (ovarian) women. This condition is relatively commonly experienced by women. Most ovarian cysts are harmless and can disappear on its own without special treatment. The presence of cysts in the ovaries is difficult to detect because it does not cause symptoms. New cysts show symptoms when it has progressed.
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled bumps that develop on the ovaries (ovarian) women. This condition is relatively commonly experienced by women. Most ovarian cysts are harmless and can disappear on its own without special treatment. The presence of cysts in the ovaries is difficult to detect because it does not cause symptoms. New cysts show symptoms when it has progressed.
Recognize the symptoms of
ovarian cysts
In most cases, we would not usually aware of the presence of
ovarian cysts in the body. Because basically the presence of cysts often cause
no symptoms. However you will have symptoms if the cyst has been enlarged,
broken, or cover the blood flow to the ovaries. Here are the symptoms that may
arise as a result of the presence of cysts:
- Frequent urination.
- Pain during defecation.
- Feel fatigue and dizziness.
- Bloated.
- Changes in the menstrual cycle.
- Nausea, vomiting, or pain in the
breast as you experience during pregnancy.
- Indigestion or easily satisfied
when you only eat a little.
- Pelvic pain during sexual
intercourse.
- Pelvic pain before menstruation
arrives or before menstruation ends.
- Pelvic pain spread to the lower
back and thighs.
Went to the doctor
After knowing the symptoms and feel one of them, the better
immediately consult a doctor. With check with your doctor to ensure that you
have a cyst or not. Prior to the doctor, there are some things you need to
prepare.
- Recognize the symptoms of the presence of ovarian cysts. If you feel it, note these symptoms. Or if you experience pain, but not contained in one of the symptoms of the presence of a cyst, you may also include them.
- Prepare questions. Prepare important questions surrounding the cyst to be proposed to the doctor. For example, what tests are required in order to detect cysts? Or whether an ovarian cyst can disappear on their own or need special care?
- Write each of the drugs and supplements you are taking. Include also the dosage and how often you eat them.
- Invite family or closest associates to accompany. It is useful to help you remember all the information that doctors give, if you forget.
- Before you get out of the doctor’s office, make sure you understand all of the information that has been given. Do not hesitate to ask if there are things that still do not understand.
After consultation with the doctor, you will undergo a physical
examination is the examination of the pelvis. At the time of pelvic
examination, the doctor will examine the genitals, vagina, lower abdominal
cavity and also using a speculum to see the reproductive tract. If large
enough, the cyst will be felt when the examination is carried out.
Every woman especially those who have been sexually active
should have a Pap smear every three years. This test is done as a precautionary
measure cervical cancer. Before the Pap smear, the doctor generally performs a
pelvic exam first. Not infrequently the cyst was discovered accidentally when
doctors examined the pelvis.
Undergoing medical tests
If you feel the symptoms of a specific and specialized to a
doctor during a pelvic exam or feel a lump, following medical tests will help
detect if there is a cyst or not.
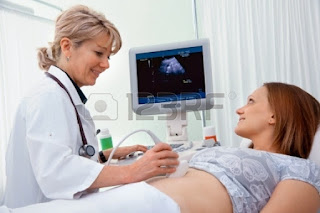
Ultrasonography (USG). This method is used to detect the
presence of ovarian cysts and determine its size. During the examination, the
doctor will place an ultrasound device on your stomach and fill your abdomen or
pelvis can be seen on the display screen.
Blood tests. Your doctor will advise you to undergo a blood test
if the results of the ultrasound shows that the cyst you have solid or high
risk of developing ovarian cancer. Through this test, the doctor will test the
protein content is often called cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) in your blood. The
reason is because levels of CA-125 can be increased in women suffering from
ovarian cancer. But not all of the increase in CA-125 is caused by ovarian
cancer. There is likely to be caused by pelvic inflammatory disease,
endometriosis, or uterine fibroids. Therefore, the conclusion of someone
suffering from ovarian cancer can not be based on the levels of CA-125nya only.
Laparoscopic. Through a small incision, the doctor will insert a
laparoscope tool that hose ends equipped with lights and cameras. Before
starting this surgical method, you’ll undergo anesthesia process. With
laparoscopy, the doctor can look directly pelvis and reproductive organs as
well as if there is an abnormality.
Not all cysts require medical treatment. There is a type of cyst
is known as ‘functional cyst’. Functional cysts associated with the menstrual
cycle and are generally harmless. This type of cyst can disappear on their own
within two to three menstrual cycles. With a complete examination, the doctor
can find out the type of cyst and the nature of the risk to develop into
ovarian cancer.
Generally, the cyst will be followed medically if the size is
large, causing symptoms in sufferers or if the doctor feels risky cancerous
cyst.
Ovarian Cancer Risk
Factors
Basically, ovarian cysts are harmless, especially if addressed early in the development. However cyst has the potential to turn into ovarian cancer, especially if the patient:
Basically, ovarian cysts are harmless, especially if addressed early in the development. However cyst has the potential to turn into ovarian cancer, especially if the patient:
- Have gone through menopause.
- Aged between 50-60 years old
- Genes BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- Having a family with a history of ovarian cancer.
- Breast cancer.
- Ever undergoing hormone therapy after menopause.
- Smoke.
- Suffer from polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Never take medicine to increase fertility.
- Has never been pregnant.
If you have any reason to
be concerned about ovarian cysts in the body, consult a physician. With early
diagnosis, the cyst can be handled properly and the risk of complications was
lower.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar